区块链的英文是 "Blockchain"。

Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the digital world, disrupting traditional industries and reshaping the way we perceive data security and transaction processing. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network.
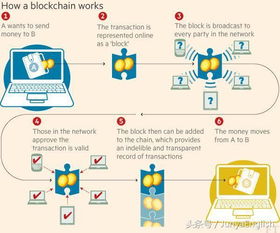
Blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a chain. The key feature of blockchain is its decentralized nature, which means that no single entity has control over the entire network. This decentralized structure ensures transparency, security, and immutability of the data stored on the blockchain.

There are several core principles that define blockchain technology:
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, where each participant has a copy of the entire ledger. This decentralization reduces the risk of a single point of failure and enhances security.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures the integrity of the data and builds trust among participants.
Transparency: All transactions on the blockchain are visible to all participants, fostering a transparent and accountable system.
Consensus Mechanism: Blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and reach an agreement on the state of the ledger. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
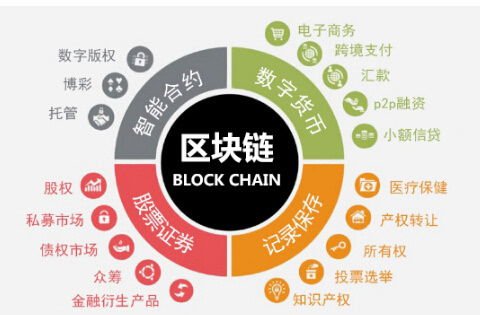
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications across various industries:
Finance: Blockchain is being used to develop cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as to streamline cross-border payments and reduce transaction costs.
Supply Chain: Blockchain can be used to track and verify the movement of goods and services, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud in the supply chain.
Healthcare: Blockchain can help in securely storing and sharing patient records, improving data privacy and interoperability.
Real Estate: Blockchain can simplify property transactions by eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction times.
Government: Blockchain can be used to create transparent and secure voting systems, as well as to manage land records and other public records.

While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges:
Scalability: Blockchain networks often struggle with scalability, as the more participants join the network, the slower the transaction processing becomes.
Energy Consumption: Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms are energy-intensive, raising concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain networks.
Regulatory Hurdles: The lack of a clear regulatory framework for blockchain technology poses challenges for businesses looking to adopt it.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain looks promising. Innovations in consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS), and advancements in blockchain architecture are expected to address some of these issues. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of blockchain in various industries.

Blockchain technology has the potential to transform the way we interact with data and conduct transactions. Its core principles of decentralization, immutability, and transparency make it a powerful tool for creating secure, efficient, and transparent systems. As the technology continues to evolve, we can look forward to seeing its impact on various industries and our daily lives.